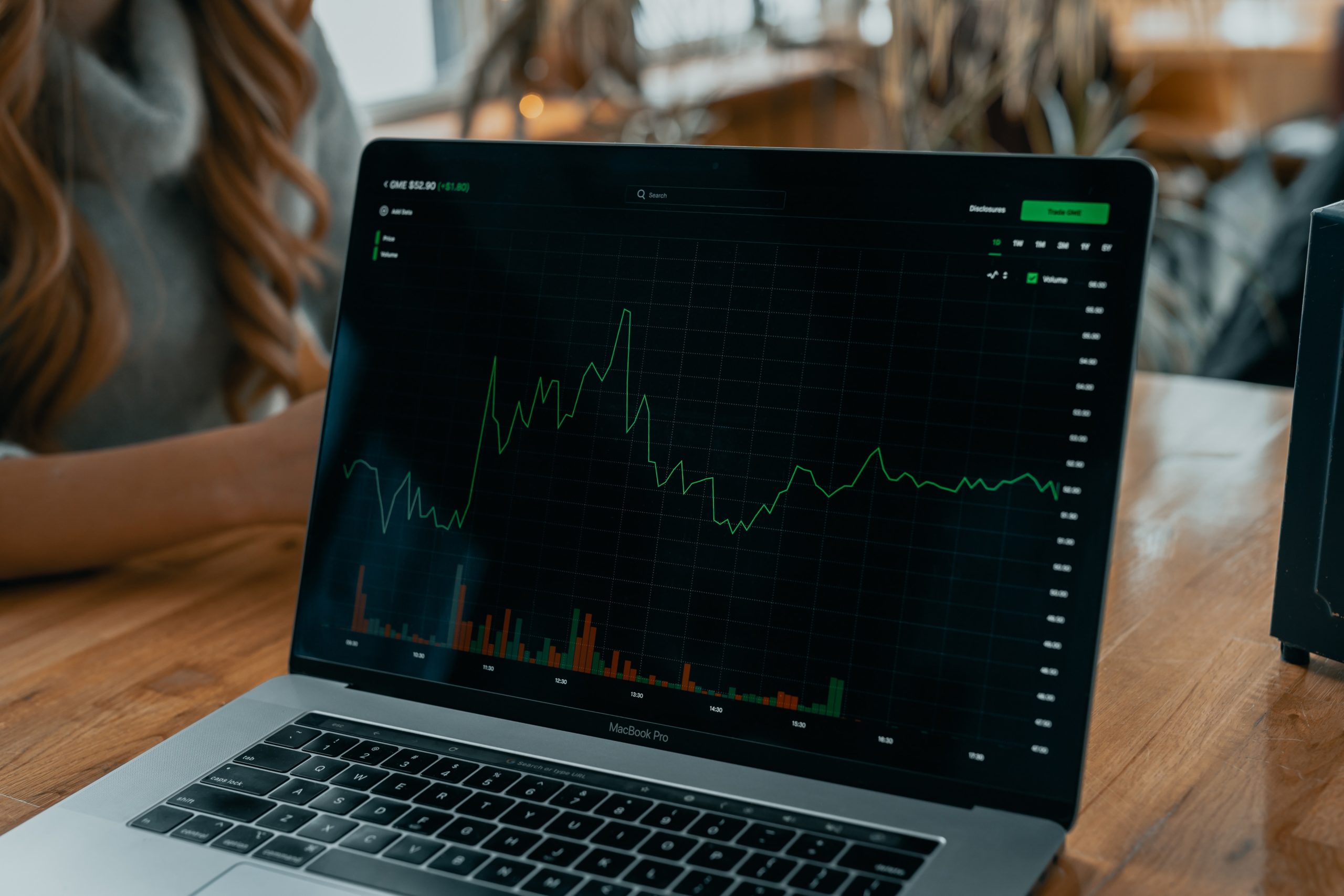
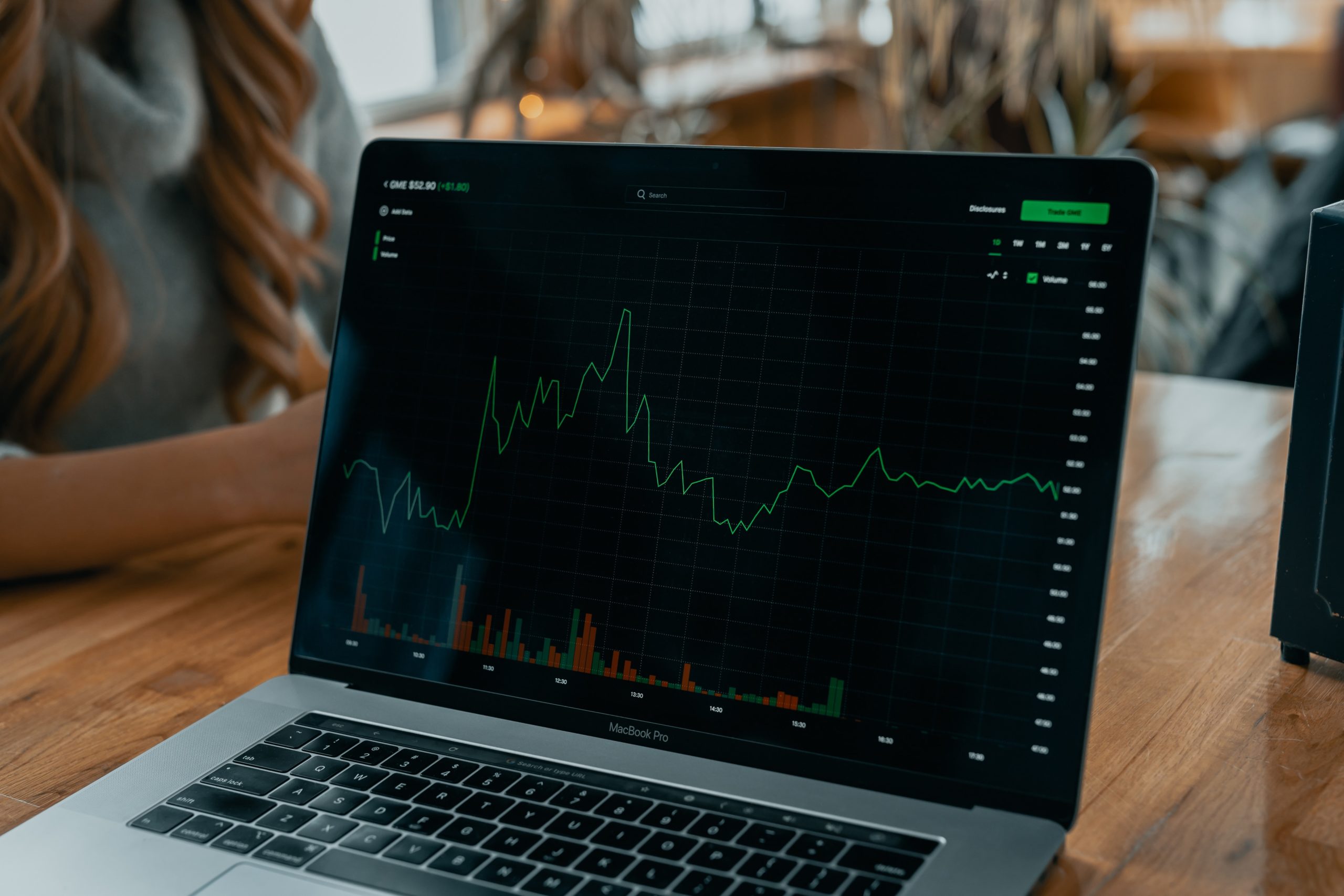
This is a blockchain platform built for high-speed, scalable transactions and the development of decentralized applications (apps). Exchanges on the network include buying, selling, and transferring crypto coins. The blockchain network enables users to develop, host, and operate dApps on its platform. EOS is its native coin, used to pay for transactions and services. A transaction fee is charged based on the volume of computing resources used during the exchange. The platform utilizes a notion called “gas” to estimate the computing resources required to execute a transaction. Each operation in a smart contract expends a certain volume of gas, and the fee users pay is based on the total volume of gas they have used during the trade. The actual cost of making an EOS trade might vary greatly based on critical aspects such as network congestion, gas prices, and the intricacy of the smart contract being executed. Its assets are used as a means of trade, and the platform makes use of encryption to safeguard the transactions of its users and authenticate the transfers they make.

Instead of gas fees, this coin exchange costs resources. EOS tokens are required for network participation. These coins can be staked for Memory, CPU, and bandwidth.
Utility token transaction costs vary substantially depending on network resource demand. Scalable and efficient, the platform can minimize transaction costs during peak network traffic. This article explains EOS transaction fees and cryptocurrency for beginners.
What it is
It is a type of coin, which allows its users access to its EOS.IO decentralized operating system. On this platform, assets are designed as a means of exchange, which uses encryption to protect users’ transactions and verify transfers. The tokens can be kept in an online or offline e-wallet for safekeeping. The coin allows its users to have access to some services offered by the network. The coin is analogous to Ethereum and often referred to as a ‘utility coin’ in the crypto world. The platform, on the other hand, is meant to be scalable and efficient, which can help keep transaction costs low during periods of high network activity.
How it works
The cost of trading this cryptocurrency is often measured in terms of memory, CPU, and network bandwidth resources rather than gas fees, as is the case on other blockchain networks. This is in contrast to other blockchain networks. The network utilizes a delegated proof-of-stake consensus mechanism, in which token users cast their votes for block producers. Block producers are responsible for validating transactions and adding new blocks to the blockchain. To participate in activities on the network, users are required to possess a predetermined minimum quantity of EOS tokens. These tokens can be staked to obtain resources such as RAM, CPU, and network bandwidth. The price of these resources usually varies according to network demand and availability. The price of RAM on the network can vary greatly depending on market demand, as it is used to store data on the blockchain. CPU resources are utilized to execute smart contracts and exchanges, and the cost of these resources varies depending on activity. Network bandwidth resources are used to carry data between nodes, and their cost varies according to demand.
The transaction cost of the coin is, in general, highly changeable and is mostly influenced by the demand that is placed on the resources of the network. The platform is meant to be scalable and efficient, for instance, so that it can assist reduce transaction costs to a minimum even when there is a lot of activity on the network. Moreover, when there is a lot of activity on the network.